You’ve been hearing people talking about your need to take iodine. Even so, there are many types of iodine, uses, and health benefits, it can be confusing. You might ask, “Why do I need to take iodine,” and “What kind of iodine is best?” Let’s see if we can help you unravel the mysteries that may surround the topic of iodine.
Thyroid and Iodine
Iodine stands as a crucial element for the optimal performance of the thyroid gland, a small but vital organ situated in the front of the lower neck. This article explores the significant relationship between iodine and thyroid function, shedding light on the gland’s ability to safeguard the body against harmful microorganisms.
1. Thyroid’s Prime Location
- The human thyroid gland resides in the anterior part of the lower neck.
- It plays a pivotal role in regulating various bodily functions.
2. Thyroid’s Role as a Blood Guardian
- Remarkably, all the blood circulating in the body passes through the thyroid gland approximately every 17 minutes.
- The thyroid gland’s unique cellular composition has a natural affinity for iodine.
3. Iodine’s Microorganism-Killing Power
- During the 17-minute transit through the thyroid gland, iodine secretion becomes a formidable defense mechanism.
- It targets and neutralizes weak microorganisms that may have entered the bloodstream through various routes, including skin injuries, nasal or throat linings, or absorption from the digestive tract.
4. Weakening Harmful Microorganisms
- Robust microorganisms also experience a weakening effect as they traverse the thyroid gland during each 17-minute cycle.
- With successive cycles, these microorganisms become progressively weaker until they are eventually eliminated, provided the gland maintains its normal iodine supply.
5. The Dependence on Dietary Iodine
- The iodine content of the thyroid gland relies heavily on the iodine available in an individual’s diet and water intake.
- In cases of insufficient iodine intake, the thyroid gland is deprived of this essential element, hindering its ability to perform its critical functions.
6. Historical Iodine Awareness
- More than a century ago, awareness grew regarding the need for increased iodine intake.
- Some governments took early steps to address this by adding small amounts of iodine to table salt.
- However, these measures were often insufficient to meet the body’s iodine requirements.
7. Post-Fukushima Imperative
- Following the nuclear accident at Fukushima, the importance of iodine supplementation gained renewed significance.
- Radioactive iodine released into the environment underscored the necessity for adequate iodine intake to counteract potential health risks.
Top 10 Health Benefits of Iodine Supplementation
Iodine, often overlooked in its significance, plays a vital role in various aspects of human health, including preventing and mitigating cancer risks.
1. Iodine and Breast Cancer
- High iodine intake is associated with a lower risk of breast cancer.
- Adequate iodine levels may contribute to reduced breast cancer susceptibility.
2. Iodine and Liver Cancer
- Conversely, low iodine intake is associated with an increased risk of liver cancer.
- Maintaining sufficient iodine levels may help lower the risk of liver cancer.
3. Iodine’s Role in Skin Cancer
- Iodine has shown promise in the treatment of skin cancer.
- Its potential benefits extend to various forms of skin cancer.
4. Protection Against Radioactive Iodine
- Iodine serves as a protective agent against radioactive iodine.
- Exposure to radioactive iodine, (as witnessed in events like the Fukushima nuclear disaster) can be mitigated with iodine supplementation.
5. Iodine’s Role in Metabolism
- Iodine is essential for metabolism and is indispensable for human life.
- It plays a critical role in every cell within the human body.
6. Hormone Production and Thyroid Health
- Iodine is crucial for the synthesis of thyroid hormones.
- Adequate iodine levels help prevent both hypo- and hyperthyroidism.
- Iodine can improve insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism.
- It attaches to insulin receptors, promoting better metabolic function.
7. Iodine and the Immune System
- Long-term iodine deficiency can compromise the immune system.
- Poor immune response is closely linked to impaired thyroid function.
- Iodine deficiency can significantly impact the immune system.
8. Iodine’s Blood-Purifying Properties
- Iodine has the capacity to purify the bloodstream.
- It performs a similar function to the thyroid, which cleanses the bloodstream every 17 minutes.
- Adequate iodine levels, especially in children, help the body resist pathogens, potentially reducing the need for vaccines.
9. Iodine’s Role in Phagocytosis
- Iodide accumulates during phagocytosis, a process where the body engulfs and consumes bacteria and foreign substances.
- Iodide attaches to bacteria and proteins, forming iodoproteins.
- The thyroid hormones may also serve as a source of iodide in certain instances.
10. Additional Functions of Iodine
- Iodine’s versatile applications include heart disease prevention.
- It eliminates toxic halogens, including radioactive I-131.
- Iodine supports apoptosis, the programmed cell death crucial in preventing cancer.
- It activates hormone receptors and aids in cancer prevention.
- Iodine enhances ATP function and production.
- It can help prevent fibrocystic breast disease.
- Iodine reduces insulin requirements in diabetics.
- It supports protein synthesis.
- Iodine deficiency is a global health concern.
- Iodine’s pathogen-fighting properties extend to molds, fungi, parasites, and malaria.
- Iodine is necessary to counteract the effects of radiation from cordless phones, cell phones, and smart meters.
- It plays a vital role in pregnancy, particularly in preventing apoptosis during fetal development.
- Iodine regulates estrogen production in the ovaries.
- Iodine has anti-mucolytic properties, reducing mucus catarrh.
- It neutralizes hydroxyl ions and hydrates cells.
- Iodine is linked to cognitive improvement.
- High doses of iodine can be applied topically for wound care, pain relief, and hair growth restoration.
- It aids in reducing tissue scarring and managing hyper-scarring conditions.
- High iodine doses may be employed to address certain diseases.
- Iodine may contribute to spiritual development.
Choosing the Right Iodine Supplement
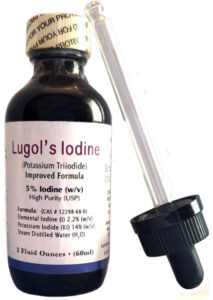
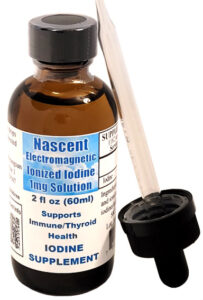
- Liquid iodine in the form of Nascent Iodine and Lugol’s Iodine are recommended supplements.
- Nascent Iodine is suitable for children and individuals sensitive to iodine, allowing for precise dosing.
- Lugol’s Iodine, with nearly two centuries of use, remains a reliable choice.
- Various solid forms of iodine supplements are also available to suit individual preferences.
Iodine’s multifaceted role in cancer prevention and overall health cannot be overstated. It serves as a powerful ally in bolstering the body’s defenses against various forms of cancer and other health threats. Iodine supplementation, along with a balanced diet and consultation with healthcare professionals, can help individuals harness the many benefits of this essential element.